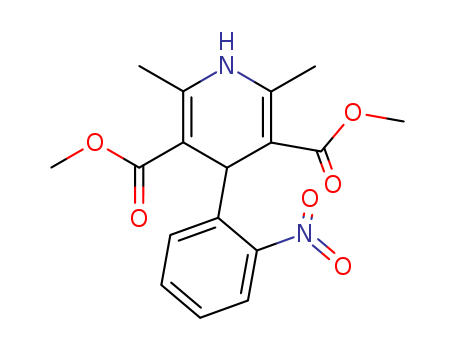
21829-25-4
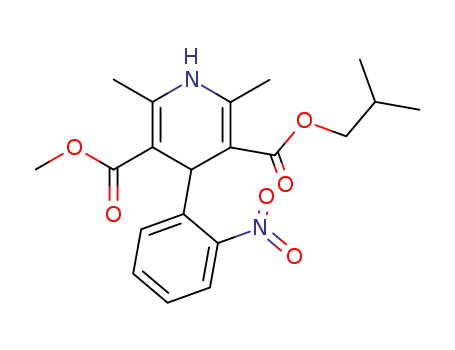
- Product Name:Nifedipine
- Molecular Formula:C17H18N2O6
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:346.34
Product Details;
CasNo: 21829-25-4
Molecular Formula: C17H18N2O6
Appearance: yellow crystalline solid
Manufacturer supply high quality Nifedipine 21829-25-4 with GMP standards
- Molecular Formula:C17H18N2O6
- Molecular Weight:346.34
- Appearance/Colour:yellow crystalline solid
- Vapor Pressure:2.68E-08mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:171-175 °C
- Refractive Index:1.584
- Boiling Point:475.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa -0.9/>13(DMF,t undefined) (Uncertain)
- Flash Point:241.2 °C
- PSA:110.45000
- Density:1.271 g/cm3
- LogP:3.02760
Nifedipine(Cas 21829-25-4) Usage
|
Pharmacological effects |
Nifedipine is a kind of dihydropyridine calcium antagonists, it can inhibit the Ca2 + uptake of cardiac and vascular smooth muscles, and it can expand the coronary artery , increase coronary blood flow,and improve myocardial ischemic tolerance, at the same time, it can expand peripheral arteries and reduce peripheral vascular resistance,and relieve coronary artery spasm, and increase coronary blood flow, improve myocardial ischemia,in order to decrease the blood pressure. Small doses do not affect blood pressure, when expanding coronary artery ,it is a better anti-angina drug .It is used for the prevention and treatment of angina pectoris,with no adverse effects on respiratory function, its efficacy is best particularly for angina pectoris coronary spasm and obstructive airway disease with angina , its efficacy is superior to β-blockers.It is also applied to all types of high blood pressure, including severe and resistant hypertension. Treatment of refractory congestive heart failure may be taking this long. It is also used for the treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension, diffuse esophageal spasm and bronchial asthma, duodenal ulcers, urinary tract obstruction, exercise-induced asthma, achalasia. Nifedipine has a certain selectivity on vascular smooth muscles , the direct negative inotropic effect and denaturation effect on the heart are weak, systemic administration of it does not cause the heart rate slowing down ,on the contrary, the heart rate performances reflected increase. The above information is edited by the lookchem of Tian Ye. |
|
Production methods |
O-nitrobenzaldehyde, methyl acetoacetate, methanol, ammonia are refluxed together , then froze , crystallize,after filtration, nifedipine crude is obtained . The crude product is recrystallized through methanol .then the product is derived , yield rate is 50%. |
|
Toxicity grading |
Highly toxic |
|
Acute toxicity |
Oral-rat LD50: 1022 mg/kg; Oral-Mouse LD50: 310 mg/kg. |
|
Flammability and hazard characteristics |
Combustion produces toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides; medicinal side effects: low blood pressure, cardiac disease, local blood flow disease, high blood sugar, psychosis. |
|
Storage Characteristics |
Ventilated , low-temperature, drying; and it is kept separately from food raw materials warehouse. |
|
Extinguishing agent |
Dry powder, foam, sand, carbon dioxide, water spray. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
45 grams 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, 80 cc acetoacetic acid methyl ester, 75 cc methanol and 32 cc ammonia are heated under reflux for several hours, filtered off, cooled and, after suction-filtration, 75 grams of yellow crystals of MP 172° to 174°C are obtained, according to US Patent 3,485,847. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Coronary vasodilator |
|
World Health Organization (WHO) |
Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It is listed in the WHO Model List of Essential Drugs. The 10mg tablet is retained on the list for short-term treatment of hypertension. Sustained-release preparations are advised for long-term treatment. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Aqueous solutions are very sensitive to light. . Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Nifedipine is sensitive to light. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Nifedipine are not available; however, Nifedipine is probably combustible. |
|
Biological Activity |
L-type calcium channel blocker. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Nifedipine is a L-type Ca2+ channel blocker; and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Nifedipine has neuroprotection activity and protects substantia nigra. Nifedipine has antioxidant potential. Nifedipine downregulates inflammatory cytokines like macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Nifedipine has antihypertensive properties. Nifedipine inhibits extracellular region of adenosine A2a receptor (ADORA2A) gene. |
|
Mechanism of action |
Nifedipin causes relaxation of smooth musculature, dilation of coronary and peripheral arteries, and reduction of peripheral resistance and arterial blood pressure, and enhances oxygen supply to the heart. |
|
Synthesis |
Nifedipine, dimethyl ether 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2′-nitrophenyl)-3,5- piridindicarboxylic acid (19.3.16), is synthesized by a Hantsch synthesis from two molecules of a β-dicarbonyl compound—methyl acetoacetate, using as the aldehyde component— 2-nitrobenzaldehyde and ammonia. The sequence of the intermediate stages of synthesis has not been completely established. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Aminophylline: possibly increases aminophylline concentration. Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect. Anti-arrhythmics: concentration of dronedarone increased. Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin; metabolism possibly inhibited by clarithromycin, erythromycin and telithromycin. Antidepressants: metabolism possibly inhibited by fluoxetine; concentration reduced by St John’s wort; enhanced hypotensive effect with MAOIs. Antiepileptics: effect reduced by carbamazepine, barbiturates, phenytoin and primidone. Antifungals: metabolism possibly inhibited by itraconazole and ketoconazole; concentration increased by micafungin; negative inotropic effect possibly increased with itraconazole. Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect, increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect of post-synaptic alpha-blockers; occasionally severe hypotension and heart failure with beta-blockers. Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by ritonavir; use telaprevir with caution. Cardiac glycosides: digoxin concentration possibly increased. Ciclosporin: may increase ciclosporin level, but not a problem in practice; nifedipine concentration may be increased. Cytotoxics: metabolism of vincristine possibly reduced. Grapefruit juice: concentration increased - avoid. Magnesium salts: profound hypotension with IV magnesium. Tacrolimus: increased tacro |
|
Metabolism |
Nifedipine is metabolised in the gut wall and oxidised in the liver via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4, to inactive metabolites. Excreted mainly as metabolites via the kidney |
|
Chemical properties |
Yellow crystals. Melting point 172-174 ℃. Soluble in acetone, chloroform, ethyl acetate, dissolved in hot methanol, insoluble in water. It easily deteriorates in case of light. |
|
Category |
Toxic substances |
|
Brand name |
Adalat (Bayer); Afeditab (Watson);Procardia (Pfizer). |
|
General Description |
Nifedipine, 1,4-dihydro-2, 6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate dimethyl ester(Adalat, Procardia), is a dihydropyridine derivative thatbears no structural resemblance to the other calcium antagonists.It is not a nitrate, but its nitro group is essential for itsantianginal effect. As a class, the dihydropyridines possessa central pyridine ring that is partially saturated. To this, positions2 and 6 are substituted with an alkyl group that mayplay a role in the agent’s duration of action. In addition, positions3 and 5 are carboxylic groups that must be protectedwith an ester functional group. Depending on the type ofester used at these sites, the agent can be distributed to variousparts of the body. Finally, position 4 requires an aromaticsubstitution possessing an electron-withdrawinggroup (i.e., Cl or NO2) in the ortho and/or meta position. |
InChI:InChI=1/C17H18N2O6/c1-9-13(16(20)24-3)15(14(10(2)18-9)17(21)25-4)11-7-5-6-8-12(11)19(22)23/h5-8,13,15H,1-4H3/t13?,15-/m1/s1
21829-25-4 Relevant articles
Protective role of the novel hybrid 3,5-dipalmitoyl-nifedipine in a cardiomyoblast culture subjected to simulated ischemia/reperfusion
Santa-Helena, Eduarda,Teixeira, Stefanie,Castro, Micheli Rosa de,Cabrera, Diego da Costa,D'Oca, Caroline Da Ros Montes,D'Oca, Marcelo G. Montes,Votto, Ana Paula S.,Nery, Luiz Eduardo Maia,Gon?alves, Carla Amorim Neves
, p. 356 - 364 (2017)
This work investigated the acute effects...
Catalytic effect of nanosized metal oxides on the Hantzsch reaction
Fedorova,Koryakova,Valova,Ovchinnikova,Titova,Rusinov,Charushin
, p. 566 - 572 (2010)
The effect of nanosized copper and alumi...
Approaches to combinatorial synthesis of heterocycles: A solid-phase synthesis of 1,4-dihydropyridines
Gordeev, Mikhail F.,Patel, Dinesh V.,Gordon, Eric M.
, p. 924 - 928 (1996)
N-Immobilized enamino esters 2 derived f...
Conformational preferences and dynamics of 4-isoxazolyl-1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists as determined by variable-temperature NMR and NOE experiments
Palmer, Robert B.,Andro, Tina M.,Natale, Nicholas R.,Andersen, Niels H.
, p. 495 - 504 (1996)
A series of 14 4-(3′,5′-disubstituted is...
Aqueous CO2fixation: construction of pyridine skeletons in cooperation with ammonium cations
Fan, Weibin,Guo, Shiwei,Huang, Deguang,Li, Yinghua,Xiang, Shiqun,Zhang, Wei
supporting information, p. 7950 - 7955 (2021/10/29)
A simple and green method is explored fo...
Photoinduced Iron-Catalyzed ipso-Nitration of Aryl Halides via Single-Electron Transfer
Wu, Cunluo,Bian, Qilong,Ding, Tao,Tang, Mingming,Zhang, Wenkai,Xu, Yuanqing,Liu, Baoying,Xu, Hao,Li, Hai-Bei,Fu, Hua
, p. 9561 - 9568 (2021/08/06)
A photoinduced iron-catalyzed ipso-nitra...
METHODS FOR TREATING CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME AND MYALGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS
-
, (2021/03/13)
In one aspect the invention relates to a...
Preparation method of nifedipine
-
Paragraph 0051-0061, (2020/07/02)
The invention provides a preparation met...
21829-25-4 Process route
-
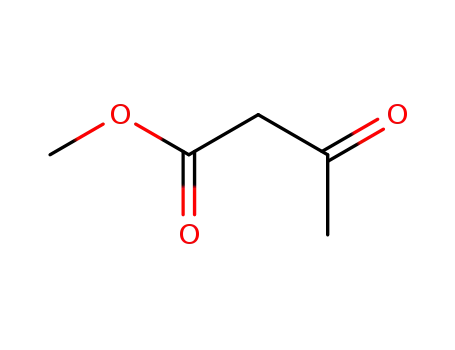
-
105-45-3
acetoacetic acid methyl ester
-
-
552-89-6
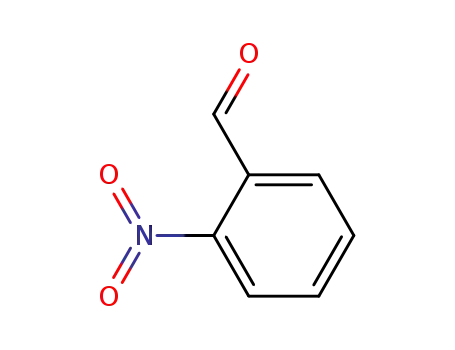
2-nitro-benzaldehyde

-
-
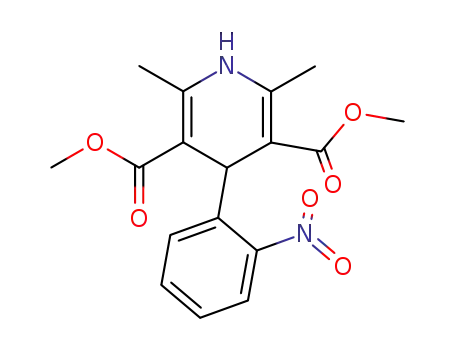
21829-25-4
nifedipine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
C23H3BF16N2O; ammonium acetate;
In
toluene;
at 100 ℃;
for 10h;
|
95% |
|
With
ammonium acetate; sodium dodecyl-sulfate; toluene-4-sulfonic acid;
for 1h;
ultrasonic irradiation;
|
92% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
at 75 ℃;
for 3h;
Neat (no solvent);
|
92% |
|
With
C35H20F15N2O6SZr(1+)*C7F15O3S(1-); ammonium acetate;
In
toluene;
at 120 ℃;
for 1h;
|
92% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
In
neat (no solvent);
at 20 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
Green chemistry;
|
91% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
In
ethanol; water;
at 120 ℃;
Temperature;
|
91% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
for 0.1h;
aluminum oxide
microwave irradiation;
|
90% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
at 20 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
|
90% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
at 90 ℃;
for 1h;
Neat (no solvent);
|
90% |
|
With
ammonium carbonate;
In
neat (no solvent);
at 90 ℃;
for 0.5h;
Green chemistry;
|
89% |
|
With
[Cp2Zr(H2O)2]+[OSO2C4F9]-2; ammonium acetate;
In
neat (no solvent);
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
|
88% |
|
With
benzyltrimethylammonium fluoride; ammonium acetate;
at 70 ℃;
for 0.216667h;
Green chemistry;
|
88% |
|
With
ammonium acetate; N-butylpyridinium tetrafluoroborate;
at 100 - 110 ℃;
for 3h;
|
87% |
|
With
alumina; ammonium acetate;
In
neat (no solvent);
at 120 ℃;
Microwave irradiation;
Green chemistry;
|
87% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
SiO2-SO3H;
In
hexane;
at 60 ℃;
for 6h;
|
86% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
In
neat (no solvent);
at 100 ℃;
for 0.25h;
Green chemistry;
|
86% |
|
With
ammonium acetate; aluminum oxide; zinc(II) bis(L-proline);
at 70 ℃;
for 3.5h;
|
85% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
at 100 ℃;
for 0.5h;
|
85% |
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
ethanol;
at 110 ℃;
Flow reactor;
|
85% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
In
ethanol;
for 0.0333333h;
microwave irradiation;
|
84% |
|
With
magnesium nitride; ethanol; water;
at 80 ℃;
|
84% |
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
ethanol;
for 2h;
Heating;
|
79% |
|
With
ammonium acetate;
Darkness;
Reflux;
|
79% |
|
With
C21H38N(1+)*Mo11O40PV(4-)*3H(1+); ammonium acetate;
In
ethanol;
at 78 ℃;
for 8h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Temperature;
Time;
Catalytic behavior;
Green chemistry;
|
78% |
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
ethanol; water;
for 3h;
Reflux;
|
76% |
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
ethanol;
for 3h;
Reflux;
|
71% |
|
With
aluminum oxide; ammonia;
In
methanol;
Heating;
|
67% |
|
With
ammonium acetate; copper(II) bis(trifluoromethanesulfonate);
In
acetonitrile;
at 25 ℃;
for 12h;
|
60% |
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
ethanol;
for 5h;
Ambient temperature;
|
54% |
|
With
ammonia;
In
methanol; water;
at -20 ℃;
Reflux;
|
45% |
|
With
carbon dioxide; potassium tert-butylate; ammonium chloride; ethanolamine; Selectfluor;
In
water;
at 120 ℃;
for 24h;
Sealed tube;
Green chemistry;
|
32% |
|
With
ammonia; sodium tosylate;
In
water;
for 0.0166667h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Microwave irradiation;
Reflux;
Green chemistry;
|
28% |
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
ethanol;
Heating;
|
27% |
|
With
pyridine; 4 A molecular sieve; polysterene-based acid-cleavable Rink amine resin; trifluoroacetic acid;
Yield given. Multistep reaction;
1) CH2Cl2, rt, 3 d; 2) 45 deg C, 24 h; 3) CH2Cl2, 45 min;;
|
|
|
With
ammonia;
In
methanol;
|
|
|
With
ammonium acetate;
|
90%. |
|
With
ammonia;
In
methanol;
Reflux;
|
|
|
With
ammonium acetate;
In
ethanol;
at 80 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
With
aminosulfonic acid; ammonium acetate;
In
methanol;
for 24h;
Reflux;
|
-
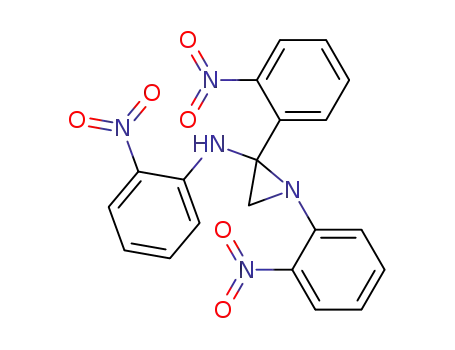
-
1-(2'-nitrophenyl)-N,N'-bis-(2'-nitrophenyl) methylene methanediamine

-

-
105-45-3
acetoacetic acid methyl ester

-

-
21829-25-4
nifedipine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
ammonium hydroxide;
In
methanol; acetic acid;
|
76% |
21829-25-4 Upstream products
-
21731-17-9
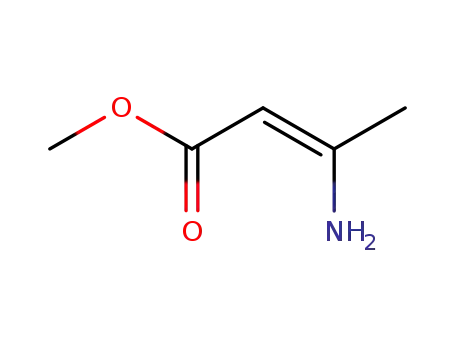
methyl 3-aminocrotonate
-
124732-83-8
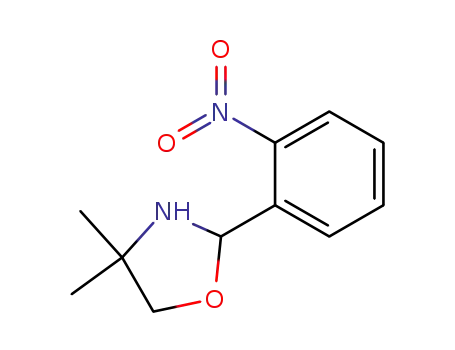
2-(o-nitro)phenyl-4,4-dimethyloxazolidine
-
124732-84-9
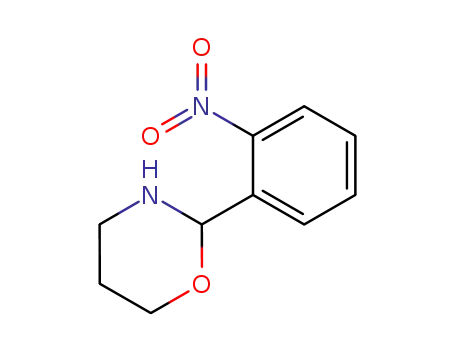
2-(o-nitro)phenyl-tetrahydro-(2H)-1,3-oxazine
-
552-89-6

2-nitro-benzaldehyde
21829-25-4 Downstream products
-
92089-09-3
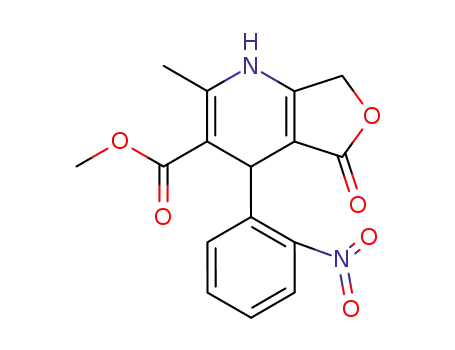
2-Methyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro<3,4-b>pyridin-3-carbonsaeuremethylester
-
113817-49-5
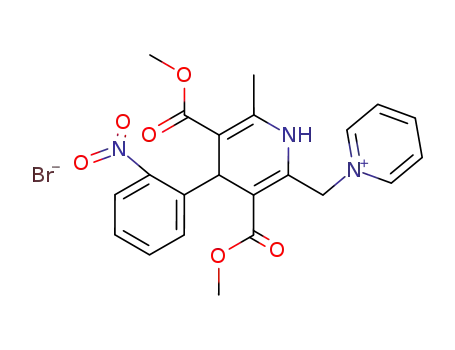
N-<2-methyl-3,5-dimethoxycarbonyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridinyl-6-methyl>pyridinium bromide
-
75956-26-2
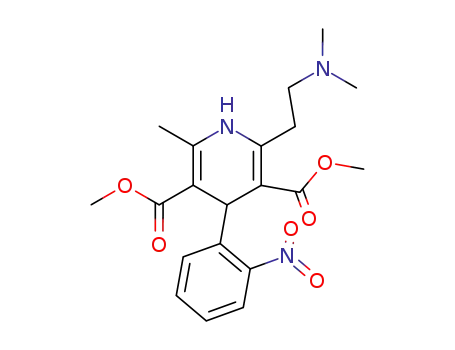
2-(2-Dimethylamino-ethyl)-6-methyl-4-(2-nitro-phenyl)-1,4-dihydro-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester
-
77233-85-3
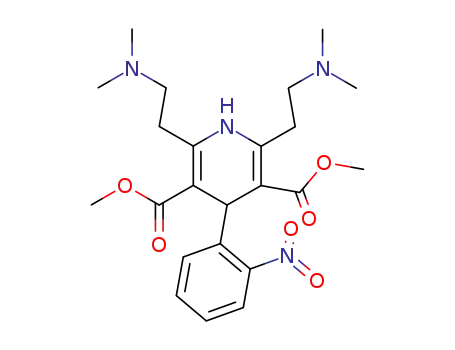
2,6-Bis-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-4-(2-nitro-phenyl)-1,4-dihydro-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester
Relevant Products
-
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose,CMC-Na
CAS:9004-32-4
-
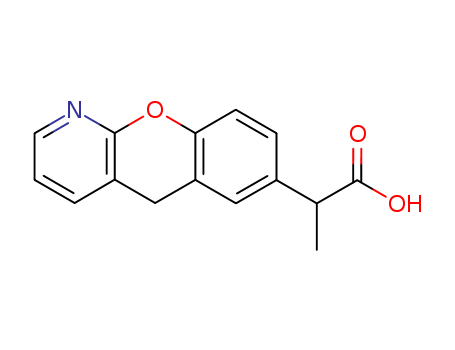
Nisoldipine
CAS:63675-72-9
-
Vorinostat
CAS:149647-78-9